topic_coherence.segmentation – Segmentation module¶
This module contains functions to perform segmentation on a list of topics.
-
gensim.topic_coherence.segmentation.s_one_one(topics)¶ Perform segmentation on a list of topics. Segmentation is defined as
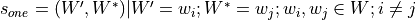 .
.- Parameters
topics (list of numpy.ndarray) – List of topics obtained from an algorithm such as LDA.
- Returns
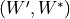 for all unique topic ids.
for all unique topic ids.- Return type
list of list of (int, int)
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> from gensim.topic_coherence import segmentation >>> >>> topics = [np.array([1, 2, 3]), np.array([4, 5, 6])] >>> segmentation.s_one_one(topics) [[(1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 1), (2, 3), (3, 1), (3, 2)], [(4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 4), (5, 6), (6, 4), (6, 5)]]
-
gensim.topic_coherence.segmentation.s_one_pre(topics)¶ Performs segmentation on a list of topics.
Notes
Segmentation is defined as
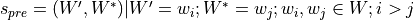 .
.- Parameters
topics (list of np.array) – list of topics obtained from an algorithm such as LDA.
- Returns
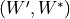 for all unique topic ids.
for all unique topic ids.- Return type
list of list of (int, int)
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> from gensim.topic_coherence import segmentation >>> >>> topics = [np.array([1, 2, 3]), np.array([4, 5, 6])] >>> segmentation.s_one_pre(topics) [[(2, 1), (3, 1), (3, 2)], [(5, 4), (6, 4), (6, 5)]]
-
gensim.topic_coherence.segmentation.s_one_set(topics)¶ Perform s_one_set segmentation on a list of topics. Segmentation is defined as
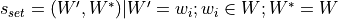
- Parameters
topics (list of numpy.ndarray) – List of topics obtained from an algorithm such as LDA.
- Returns
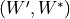 for all unique topic ids.
for all unique topic ids.- Return type
list of list of (int, int)
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> from gensim.topic_coherence import segmentation >>> >>> topics = [np.array([9, 10, 7])] >>> segmentation.s_one_set(topics) [[(9, array([ 9, 10, 7])), (10, array([ 9, 10, 7])), (7, array([ 9, 10, 7]))]]
