models.hdpmodel – Hierarchical Dirichlet Process¶
Module for online Hierarchical Dirichlet Processing.
The core estimation code is directly adapted from the blei-lab/online-hdp from Wang, Paisley, Blei: “Online Variational Inference for the Hierarchical Dirichlet Process”, JMLR (2011).
Examples
Train HdpModel
>>> from gensim.test.utils import common_corpus, common_dictionary
>>> from gensim.models import HdpModel
>>>
>>> hdp = HdpModel(common_corpus, common_dictionary)
You can then infer topic distributions on new, unseen documents, with
>>> unseen_document = [(1, 3.), (2, 4)]
>>> doc_hdp = hdp[unseen_document]
To print 20 topics with top 10 most probable words.
>>> topic_info = hdp.print_topics(num_topics=20, num_words=10)
The model can be updated (trained) with new documents via
>>> hdp.update([[(1, 2)], [(1, 1), (4, 5)]])
-
class
gensim.models.hdpmodel.HdpModel(corpus, id2word, max_chunks=None, max_time=None, chunksize=256, kappa=1.0, tau=64.0, K=15, T=150, alpha=1, gamma=1, eta=0.01, scale=1.0, var_converge=0.0001, outputdir=None, random_state=None)¶ Bases:
gensim.interfaces.TransformationABC,gensim.models.basemodel.BaseTopicModelHierarchical Dirichlet Process model
Topic models promise to help summarize and organize large archives of texts that cannot be easily analyzed by hand. Hierarchical Dirichlet process (HDP) is a powerful mixed-membership model for the unsupervised analysis of grouped data. Unlike its finite counterpart, latent Dirichlet allocation, the HDP topic model infers the number of topics from the data. Here we have used Online HDP, which provides the speed of online variational Bayes with the modeling flexibility of the HDP. The idea behind Online variational Bayes in general is to optimize the variational objective function with stochastic optimization.The challenge we face is that the existing coordinate ascent variational Bayes algorithms for the HDP require complicated approximation methods or numerical optimization. This model utilises stick breaking construction of Hdp which enables it to allow for coordinate-ascent variational Bayes without numerical approximation.
Stick breaking construction
To understand the HDP model we need to understand how it is modelled using the stick breaking construction. A very good analogy to understand the stick breaking construction is chinese restaurant franchise.
For this assume that there is a restaurant franchise (corpus) which has a large number of restaurants (documents, j) under it. They have a global menu of dishes (topics,
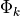 ) which they serve.
Also, a single dish (topic,
) which they serve.
Also, a single dish (topic, 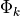 ) is only served at a single table t for all the customers
(words,
) is only served at a single table t for all the customers
(words, 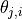 ) who sit at that table.
So, when a customer enters the restaurant he/she has the choice to make where he/she wants to sit.
He/she can choose to sit at a table where some customers are already sitting , or he/she can choose to sit
at a new table. Here the probability of choosing each option is not same.
) who sit at that table.
So, when a customer enters the restaurant he/she has the choice to make where he/she wants to sit.
He/she can choose to sit at a table where some customers are already sitting , or he/she can choose to sit
at a new table. Here the probability of choosing each option is not same.Now, in this the global menu of dishes correspond to the global atoms
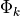 , and each restaurant
correspond to a single document j. So the number of dishes served in a particular restaurant correspond to the
number of topics in a particular document. And the number of people sitting at each table correspond to the number
of words belonging to each topic inside the document j.
, and each restaurant
correspond to a single document j. So the number of dishes served in a particular restaurant correspond to the
number of topics in a particular document. And the number of people sitting at each table correspond to the number
of words belonging to each topic inside the document j.Now, coming on to the stick breaking construction, the concept understood from the chinese restaurant franchise is easily carried over to the stick breaking construction for hdp (“Figure 1” from “Online Variational Inference for the Hierarchical Dirichlet Process”).
A two level hierarchical dirichlet process is a collection of dirichlet processes
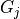 , one for each
group, which share a base distribution
, one for each
group, which share a base distribution 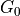 , which is also a dirichlet process. Also, all
, which is also a dirichlet process. Also, all 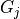 share the same set of atoms,
share the same set of atoms, 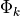 , and only the atom weights
, and only the atom weights 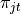 differs.
differs.There will be multiple document-level atoms
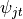 which map to the same corpus-level atom
which map to the same corpus-level atom
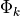 . Here, the
. Here, the 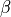 signify the weights given to each of the topics globally. Also, each
factor
signify the weights given to each of the topics globally. Also, each
factor 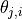 is distributed according to
is distributed according to 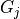 , i.e., it takes on the value of
, i.e., it takes on the value of
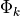 with probability
with probability 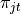 .
. 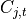 is an indicator variable whose value k
signifies the index of
is an indicator variable whose value k
signifies the index of 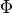 . This helps to map
. This helps to map 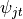 to
to 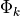 .
.The top level (corpus level) stick proportions correspond the values of
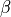 ,
bottom level (document level) stick proportions correspond to the values of
,
bottom level (document level) stick proportions correspond to the values of 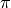 .
The truncation level for the corpus (K) and document (T) corresponds to the number of
.
The truncation level for the corpus (K) and document (T) corresponds to the number of 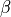 and
and 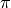 which are in existence.
which are in existence.Now, whenever coordinate ascent updates are to be performed, they happen at two level. The document level as well as corpus level.
At document level, we update the following:
The parameters to the document level sticks, i.e, a and b parameters of
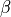 distribution of the
variable
distribution of the
variable 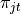 .
.The parameters to per word topic indicators,
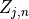 . Here
. Here 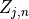 selects topic parameter
selects topic parameter
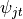 .
.The parameters to per document topic indices
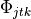 .
.
At corpus level, we update the following:
The parameters to the top level sticks, i.e., the parameters of the
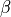 distribution for the
corpus level
distribution for the
corpus level 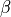 , which signify the topic distribution at corpus level.
, which signify the topic distribution at corpus level.The parameters to the topics
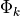 .
.
Now coming on to the steps involved, procedure for online variational inference for the Hdp model is as follows:
We initialise the corpus level parameters, topic parameters randomly and set current time to 1.
Fetch a random document j from the corpus.
Compute all the parameters required for document level updates.
Compute natural gradients of corpus level parameters.
Initialise the learning rate as a function of kappa, tau and current time. Also, increment current time by 1 each time it reaches this step.
Update corpus level parameters.
Repeat 2 to 6 until stopping condition is not met.
Here the stopping condition corresponds to
time limit expired
chunk limit reached
whole corpus processed
-
lda_alpha¶ Same as
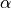 from
from gensim.models.ldamodel.LdaModel.- Type
numpy.ndarray
-
lda_beta¶ Same as
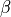 from from
from from gensim.models.ldamodel.LdaModel.- Type
numpy.ndarray
-
m_D¶ Number of documents in the corpus.
- Type
int
-
m_Elogbeta¶ Stores value of dirichlet expectation, i.e., compute
![E[log \theta]](../_images/math/40f4e27e4af9fdb0ef6ce6fbbd27c02675c5268d.png) for a vector
for a vector
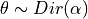 .
.- Type
numpy.ndarray:
-
m_lambda¶ Drawn samples from the parameterized gamma distribution.
- Type
{numpy.ndarray, float}
-
m_lambda_sum¶ An array with the same shape as m_lambda, with the specified axis (1) removed.
- Type
{numpy.ndarray, float}
-
m_num_docs_processed¶ Number of documents finished processing.This is incremented in size of chunks.
- Type
int
-
m_r¶ Acts as normaliser in lazy updating of m_lambda attribute.
- Type
list
-
m_rhot¶ Assigns weight to the information obtained from the mini-chunk and its value it between 0 and 1.
- Type
float
-
m_status_up_to_date¶ Flag to indicate whether lambda `and :math:`E[log theta] have been updated if True, otherwise - not.
- Type
bool
-
m_timestamp¶ Helps to keep track and perform lazy updates on lambda.
- Type
numpy.ndarray
-
m_updatect¶ Keeps track of current time and is incremented every time
update_lambda()is called.- Type
int
-
m_var_sticks¶ Array of values for stick.
- Type
numpy.ndarray
-
m_varphi_ss¶ Used to update top level sticks.
- Type
numpy.ndarray
-
m_W¶ Length of dictionary for the input corpus.
- Type
int
- Parameters
corpus (iterable of list of (int, float)) – Corpus in BoW format.
id2word (
Dictionary) – Dictionary for the input corpus.max_chunks (int, optional) – Upper bound on how many chunks to process. It wraps around corpus beginning in another corpus pass, if there are not enough chunks in the corpus.
max_time (int, optional) – Upper bound on time (in seconds) for which model will be trained.
chunksize (int, optional) – Number of documents in one chuck.
kappa (float,optional) – Learning parameter which acts as exponential decay factor to influence extent of learning from each batch.
tau (float, optional) – Learning parameter which down-weights early iterations of documents.
K (int, optional) – Second level truncation level
T (int, optional) – Top level truncation level
alpha (int, optional) – Second level concentration
gamma (int, optional) – First level concentration
eta (float, optional) – The topic Dirichlet
scale (float, optional) – Weights information from the mini-chunk of corpus to calculate rhot.
var_converge (float, optional) – Lower bound on the right side of convergence. Used when updating variational parameters for a single document.
outputdir (str, optional) – Stores topic and options information in the specified directory.
random_state ({None, int, array_like,
RandomState, optional}) – Adds a little random jitter to randomize results around same alpha when trying to fetch a closest corresponding lda model fromsuggested_lda_model()
-
doc_e_step(ss, Elogsticks_1st, unique_words, doc_word_ids, doc_word_counts, var_converge)¶ Performs E step for a single doc.
- Parameters
ss (
SuffStats) – Stats for all document(s) in the chunk.Elogsticks_1st (numpy.ndarray) – Computed Elogsticks value by stick-breaking process.
unique_words (dict of (int, int)) – Number of unique words in the chunk.
doc_word_ids (iterable of int) – Word ids of for a single document.
doc_word_counts (iterable of int) – Word counts of all words in a single document.
var_converge (float) – Lower bound on the right side of convergence. Used when updating variational parameters for a single document.
- Returns
Computed value of likelihood for a single document.
- Return type
float
-
evaluate_test_corpus(corpus)¶ Evaluates the model on test corpus.
- Parameters
corpus (iterable of list of (int, float)) – Test corpus in BoW format.
- Returns
The value of total likelihood obtained by evaluating the model for all documents in the test corpus.
- Return type
float
-
get_topics()¶ Get the term topic matrix learned during inference.
- Returns
num_topics x vocabulary_size array of floats
- Return type
np.ndarray
-
hdp_to_lda()¶ Get corresponding alpha and beta values of a LDA almost equivalent to current HDP.
- Returns
Alpha and Beta arrays.
- Return type
(numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray)
-
inference(chunk)¶ Infers the gamma value based for chunk.
- Parameters
chunk (iterable of list of (int, float)) – Corpus in BoW format.
- Returns
First level concentration, i.e., Gamma value.
- Return type
numpy.ndarray
- Raises
RuntimeError – If model doesn’t trained yet.
-
classmethod
load(fname, mmap=None)¶ Load an object previously saved using
save()from a file.- Parameters
fname (str) – Path to file that contains needed object.
mmap (str, optional) – Memory-map option. If the object was saved with large arrays stored separately, you can load these arrays via mmap (shared memory) using mmap=’r’. If the file being loaded is compressed (either ‘.gz’ or ‘.bz2’), then `mmap=None must be set.
See also
save()Save object to file.
- Returns
Object loaded from fname.
- Return type
object
- Raises
AttributeError – When called on an object instance instead of class (this is a class method).
-
optimal_ordering()¶ Performs ordering on the topics.
-
print_topic(topicno, topn=10)¶ Get a single topic as a formatted string.
- Parameters
topicno (int) – Topic id.
topn (int) – Number of words from topic that will be used.
- Returns
String representation of topic, like ‘-0.340 * “category” + 0.298 * “$M$” + 0.183 * “algebra” + … ‘.
- Return type
str
-
print_topics(num_topics=20, num_words=10)¶ Get the most significant topics (alias for show_topics() method).
- Parameters
num_topics (int, optional) – The number of topics to be selected, if -1 - all topics will be in result (ordered by significance).
num_words (int, optional) – The number of words to be included per topics (ordered by significance).
- Returns
Sequence with (topic_id, [(word, value), … ]).
- Return type
list of (int, list of (str, float))
-
save(fname_or_handle, separately=None, sep_limit=10485760, ignore=frozenset({}), pickle_protocol=2)¶ Save the object to a file.
- Parameters
fname_or_handle (str or file-like) – Path to output file or already opened file-like object. If the object is a file handle, no special array handling will be performed, all attributes will be saved to the same file.
separately (list of str or None, optional) –
If None, automatically detect large numpy/scipy.sparse arrays in the object being stored, and store them into separate files. This prevent memory errors for large objects, and also allows memory-mapping the large arrays for efficient loading and sharing the large arrays in RAM between multiple processes.
If list of str: store these attributes into separate files. The automated size check is not performed in this case.
sep_limit (int, optional) – Don’t store arrays smaller than this separately. In bytes.
ignore (frozenset of str, optional) – Attributes that shouldn’t be stored at all.
pickle_protocol (int, optional) – Protocol number for pickle.
See also
load()Load object from file.
-
save_options()¶ Writes all the values of the attributes for the current model in “options.dat” file.
Warning
This method is deprecated, use
save()instead.
-
save_topics(doc_count=None)¶ Save discovered topics.
Warning
This method is deprecated, use
save()instead.- Parameters
doc_count (int, optional) – Indicates number of documents finished processing and are to be saved.
-
show_topic(topic_id, topn=20, log=False, formatted=False, num_words=None)¶ Print the num_words most probable words for topic topic_id.
- Parameters
topic_id (int) – Acts as a representative index for a particular topic.
topn (int, optional) – Number of most probable words to show from given topic_id.
log (bool, optional) – If True - logs a message with level INFO on the logger object.
formatted (bool, optional) – If True - get the topics as a list of strings, otherwise - get the topics as lists of (weight, word) pairs.
num_words (int, optional) – DEPRECATED, USE topn INSTEAD.
Warning
The parameter num_words is deprecated, will be removed in 4.0.0, please use topn instead.
- Returns
Topic terms output displayed whose format depends on formatted parameter.
- Return type
list of (str, numpy.float) or list of str
-
show_topics(num_topics=20, num_words=20, log=False, formatted=True)¶ Print the num_words most probable words for num_topics number of topics.
- Parameters
num_topics (int, optional) – Number of topics for which most probable num_words words will be fetched, if -1 - print all topics.
num_words (int, optional) – Number of most probable words to show from num_topics number of topics.
log (bool, optional) – If True - log a message with level INFO on the logger object.
formatted (bool, optional) – If True - get the topics as a list of strings, otherwise - get the topics as lists of (weight, word) pairs.
- Returns
Output format for topic terms depends on the value of formatted parameter.
- Return type
list of (str, numpy.float) or list of str
-
suggested_lda_model()¶ Get a trained ldamodel object which is closest to the current hdp model.
The num_topics=m_T, so as to preserve the matrices shapes when we assign alpha and beta.
- Returns
Closest corresponding LdaModel to current HdpModel.
- Return type
-
update(corpus)¶ Train the model with new documents, by EM-iterating over corpus until any of the conditions is satisfied.
time limit expired
chunk limit reached
whole corpus processed
- Parameters
corpus (iterable of list of (int, float)) – Corpus in BoW format.
-
update_chunk(chunk, update=True, opt_o=True)¶ Performs lazy update on necessary columns of lambda and variational inference for documents in the chunk.
- Parameters
chunk (iterable of list of (int, float)) – Corpus in BoW format.
update (bool, optional) – If True - call
update_lambda().opt_o (bool, optional) – Passed as argument to
update_lambda(). If True then the topics will be ordered, False otherwise.
- Returns
A tuple of likelihood and sum of all the word counts from each document in the corpus.
- Return type
(float, int)
-
update_expectations()¶ Since we’re doing lazy updates on lambda, at any given moment the current state of lambda may not be accurate. This function updates all of the elements of lambda and Elogbeta so that if (for example) we want to print out the topics we’ve learned we’ll get the correct behavior.
-
update_finished(start_time, chunks_processed, docs_processed)¶ Flag to determine whether the model has been updated with the new corpus or not.
- Parameters
start_time (float) – Indicates the current processor time as a floating point number expressed in seconds. The resolution is typically better on Windows than on Unix by one microsecond due to differing implementation of underlying function calls.
chunks_processed (int) – Indicates progress of the update in terms of the number of chunks processed.
docs_processed (int) – Indicates number of documents finished processing.This is incremented in size of chunks.
- Returns
If True - model is updated, False otherwise.
- Return type
bool
-
update_lambda(sstats, word_list, opt_o)¶ Update appropriate columns of lambda and top level sticks based on documents.
- Parameters
sstats (
SuffStats) – Statistic for all document(s) in the chunk.word_list (list of int) – Contains word id of all the unique words in the chunk of documents on which update is being performed.
opt_o (bool, optional) – If True - invokes a call to
optimal_ordering()to order the topics.
-
class
gensim.models.hdpmodel.HdpTopicFormatter(dictionary=None, topic_data=None, topic_file=None, style=None)¶ Bases:
objectHelper class for
gensim.models.hdpmodel.HdpModelto format the output of topics.Initialise the
gensim.models.hdpmodel.HdpTopicFormatterand store topic data in sorted order.- Parameters
dictionary (
Dictionary,optional) – Dictionary for the input corpus.topic_data (numpy.ndarray, optional) – The term topic matrix.
topic_file ({file-like object, str, pathlib.Path}) – File, filename, or generator to read. If the filename extension is .gz or .bz2, the file is first decompressed. Note that generators should return byte strings for Python 3k.
style (bool, optional) – If True - get the topics as a list of strings, otherwise - get the topics as lists of (word, weight) pairs.
- Raises
ValueError – Either dictionary is None or both topic_data and topic_file is None.
-
STYLE_GENSIM= 1¶
-
STYLE_PRETTY= 2¶
-
format_topic(topic_id, topic_terms)¶ Format the display for a single topic in two different ways.
- Parameters
topic_id (int) – Acts as a representative index for a particular topic.
topic_terms (list of (str, numpy.float)) – Contains the most probable words from a single topic.
- Returns
Output format for topic terms depends on the value of self.style attribute.
- Return type
list of (str, numpy.float) or list of str
-
print_topic(topic_id, topn=None, num_words=None)¶ Print the topn most probable words from topic id topic_id.
Warning
The parameter num_words is deprecated, will be removed in 4.0.0, please use topn instead.
- Parameters
topic_id (int) – Acts as a representative index for a particular topic.
topn (int, optional) – Number of most probable words to show from given topic_id.
num_words (int, optional) – DEPRECATED, USE topn INSTEAD.
- Returns
Output format for terms from a single topic depends on the value of formatted parameter.
- Return type
list of (str, numpy.float) or list of str
-
print_topics(num_topics=10, num_words=10)¶ Give the most probable num_words words from num_topics topics. Alias for
show_topics().- Parameters
num_topics (int, optional) – Top num_topics to be printed.
num_words (int, optional) – Top num_words most probable words to be printed from each topic.
- Returns
Output format for num_words words from num_topics topics depends on the value of self.style attribute.
- Return type
list of (str, numpy.float) or list of str
-
show_topic(topic_id, topn=20, log=False, formatted=False, num_words=None)¶ Give the most probable num_words words for the id topic_id.
Warning
The parameter num_words is deprecated, will be removed in 4.0.0, please use topn instead.
- Parameters
topic_id (int) – Acts as a representative index for a particular topic.
topn (int, optional) – Number of most probable words to show from given topic_id.
log (bool, optional) – If True logs a message with level INFO on the logger object, False otherwise.
formatted (bool, optional) – If True return the topics as a list of strings, False as lists of (word, weight) pairs.
num_words (int, optional) – DEPRECATED, USE topn INSTEAD.
- Returns
Output format for terms from a single topic depends on the value of self.style attribute.
- Return type
list of (str, numpy.float) or list of str
-
show_topic_terms(topic_data, num_words)¶ Give the topic terms along with their probabilities for a single topic data.
- Parameters
topic_data (list of (str, numpy.float)) – Contains probabilities for each word id belonging to a single topic.
num_words (int) – Number of words for which probabilities are to be extracted from the given single topic data.
- Returns
A sequence of topic terms and their probabilities.
- Return type
list of (str, numpy.float)
-
show_topics(num_topics=10, num_words=10, log=False, formatted=True)¶ Give the most probable num_words words from num_topics topics.
- Parameters
num_topics (int, optional) – Top num_topics to be printed.
num_words (int, optional) – Top num_words most probable words to be printed from each topic.
log (bool, optional) – If True - log a message with level INFO on the logger object.
formatted (bool, optional) – If True - get the topics as a list of strings, otherwise as lists of (word, weight) pairs.
- Returns
Output format for terms from num_topics topics depends on the value of self.style attribute.
- Return type
list of (int, list of (str, numpy.float) or list of str)
-
class
gensim.models.hdpmodel.SuffStats(T, Wt, Dt)¶ Bases:
objectStores sufficient statistics for the current chunk of document(s) whenever Hdp model is updated with new corpus. These stats are used when updating lambda and top level sticks. The statistics include number of documents in the chunk, length of words in the documents and top level truncation level.
- Parameters
T (int) – Top level truncation level.
Wt (int) – Length of words in the documents.
Dt (int) – Chunk size.
-
set_zero()¶ Fill the sticks and beta array with 0 scalar value.
-
gensim.models.hdpmodel.expect_log_sticks(sticks)¶ For stick-breaking hdp, get the
![\mathbb{E}[log(sticks)]](../_images/math/d135ca365f8c5655c7defee79855d67ef25be5c7.png) .
.- Parameters
sticks (numpy.ndarray) – Array of values for stick.
- Returns
Computed
![\mathbb{E}[log(sticks)]](../_images/math/d135ca365f8c5655c7defee79855d67ef25be5c7.png) .
.- Return type
numpy.ndarray
-
gensim.models.hdpmodel.lda_e_step(doc_word_ids, doc_word_counts, alpha, beta, max_iter=100)¶ Performs EM-iteration on a single document for calculation of likelihood for a maximum iteration of max_iter.
- Parameters
doc_word_ids (int) – Id of corresponding words in a document.
doc_word_counts (int) – Count of words in a single document.
alpha (numpy.ndarray) – Lda equivalent value of alpha.
beta (numpy.ndarray) – Lda equivalent value of beta.
max_iter (int, optional) – Maximum number of times the expectation will be maximised.
- Returns
Computed (
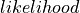 ,
, 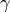 ).
).- Return type
(numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray)
